



Next: Laboratory 2: Simple Transistor
Up: Laboratory 1: Diodes and
Previous: Experiment on Simple Op-Amps
For preparation of this lab, answer the following questions.
- 1.
- Sketch the voltage signal before and after the diode in Fig. 1.1,
as a function of time.
Take the input signal to be
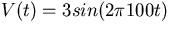 , where t is in seconds.
, where t is in seconds.
- 2.
- Sketch the input voltage signal and the signal across the resistor versus time
for
the circuit in Fig. 1.2.
Take the input signal to be
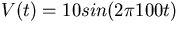 , where t is in seconds.
, where t is in seconds.
- 3.
- Sketch the voltage signals on either side of the transformer,
and the signal across the capacitor versus time
for
the circuit in Fig. 1.3.
Take the signal frequency into the transformer as 60Hz.
- 4.
- Sketch the voltage signals on either side of the transformer,
and the signal across the parallel resistor-capacitor versus time
for
the circuit in Fig. 1.4.
Take the signal frequency into the transformer as 60Hz.
Calculate the AC ripple.
- 5.
- Sketch the voltage signals on either side of the transformer,
and the signal across the parallel resistor-capacitor versus time
for
the circuit in Fig. 1.5.
Take the signal frequency into the transformer to be
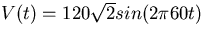 ,and the step-down turns ratio to be 5:1.
Calculate the AC ripple.
,and the step-down turns ratio to be 5:1.
Calculate the AC ripple.
- 6.
- Sketch the voltage signals on either side of the transformer,
versus time
for
the circuit in Fig. 1.6.
Take the signal frequency into the transformer to be
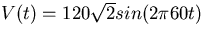 ,and the step-down turns ratio to be 5:1.
Also, sketch the the signals on the two output lines.
,and the step-down turns ratio to be 5:1.
Also, sketch the the signals on the two output lines.
- 7.
- Calculate the low frequency voltage gain for the circuit in Fig. (1.8).
Take Rf=10K, and R1=5K.
- 8.
- Calculate the low frequency voltage gain for the circuit is Fig. (1.9).
Take Rf=50K, and R1=10K.




Next: Laboratory 2: Simple Transistor
Up: Laboratory 1: Diodes and
Previous: Experiment on Simple Op-Amps
Neil Goldsman
10/23/1998